-40%
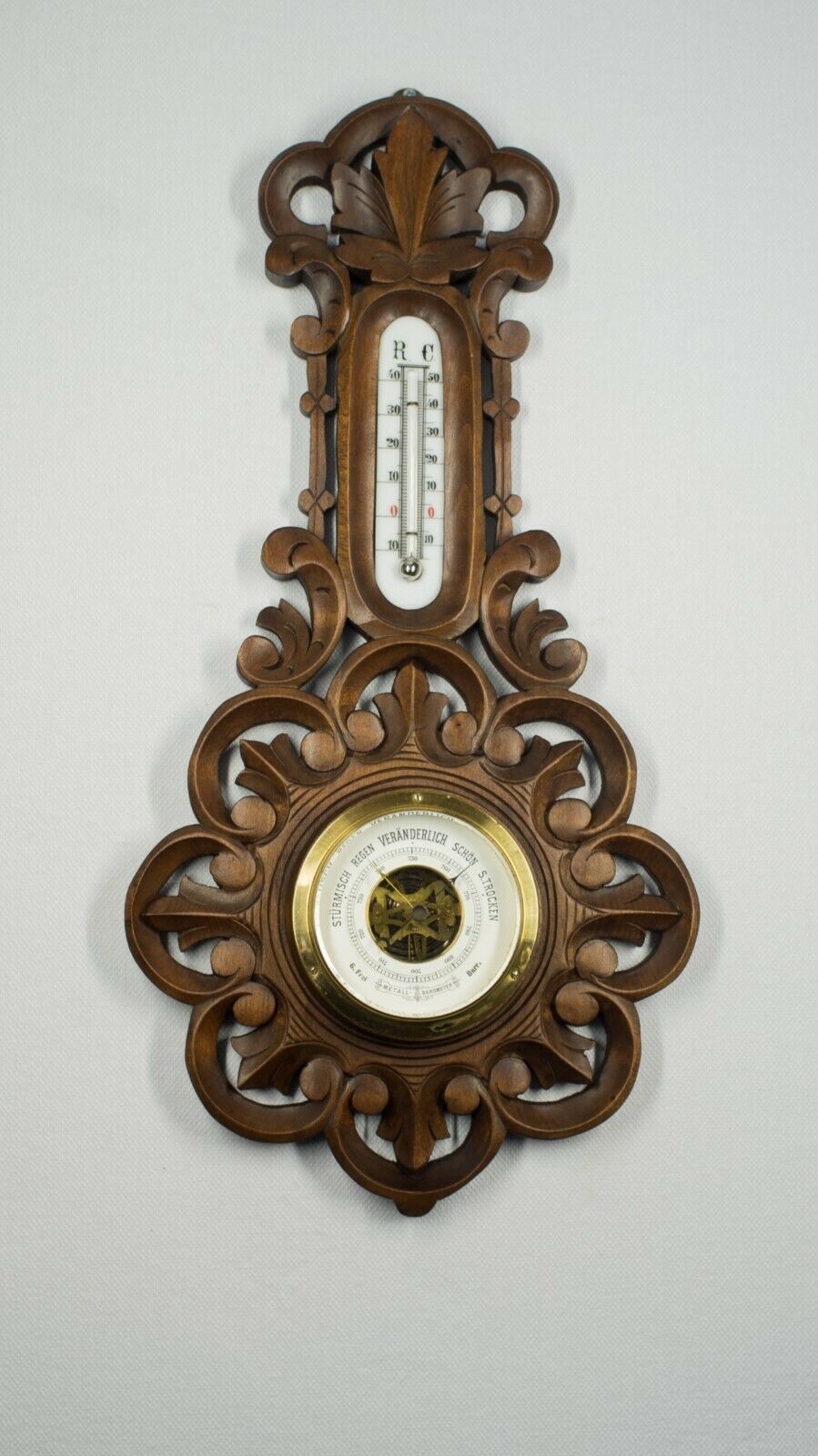
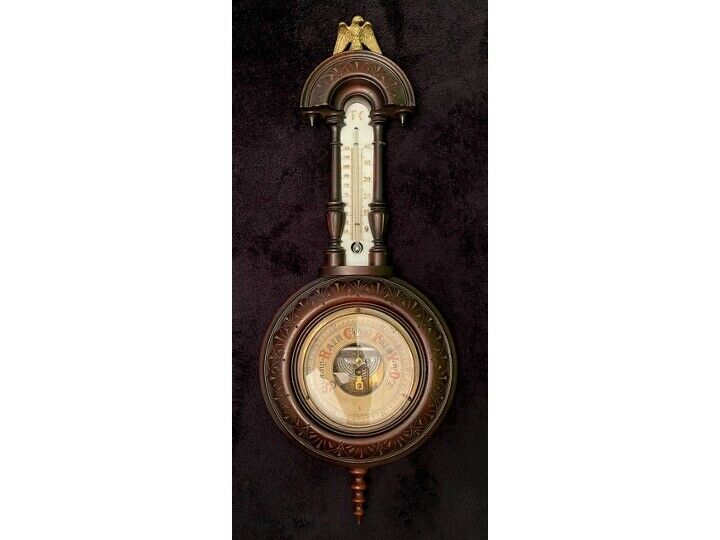
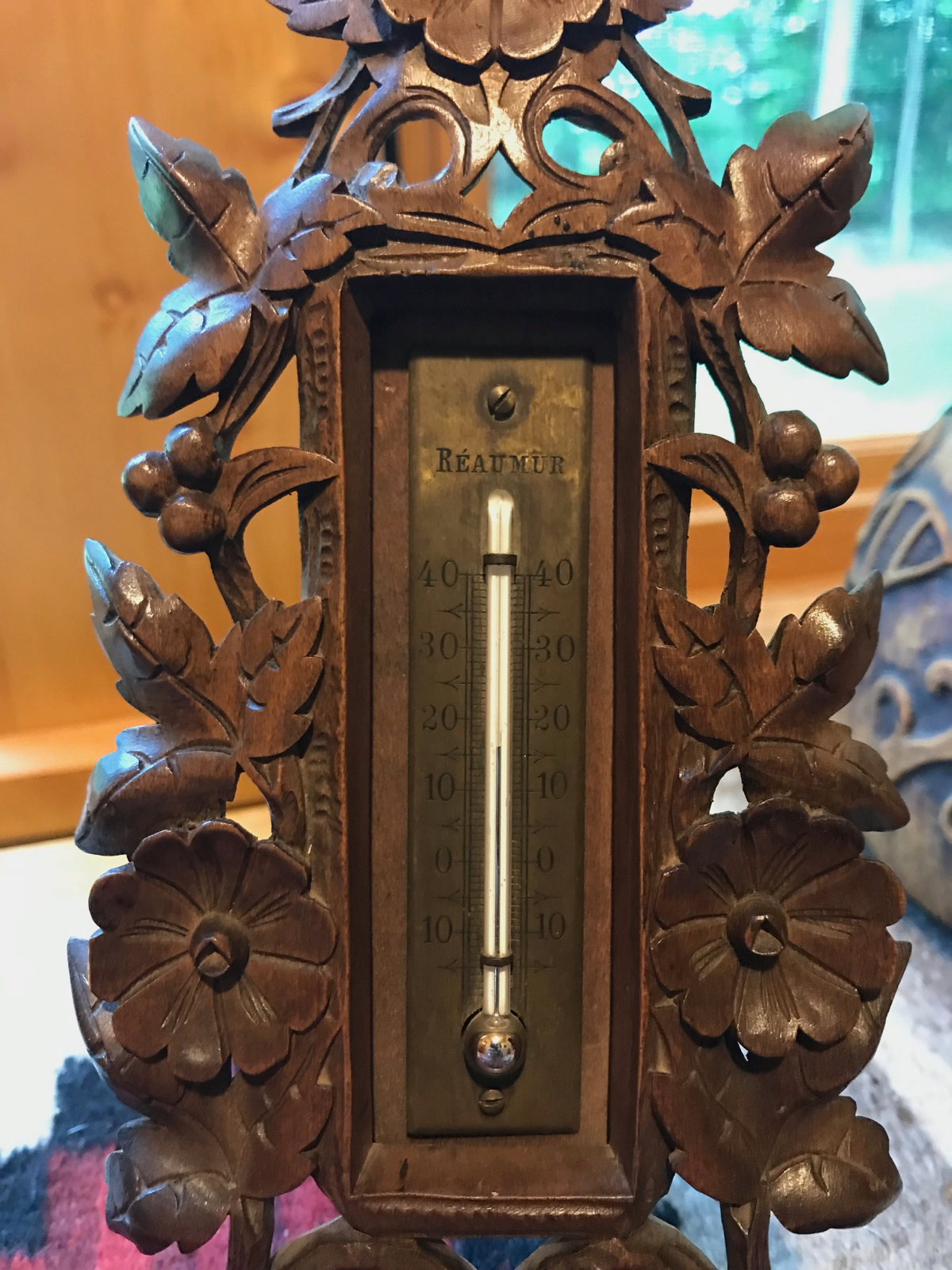
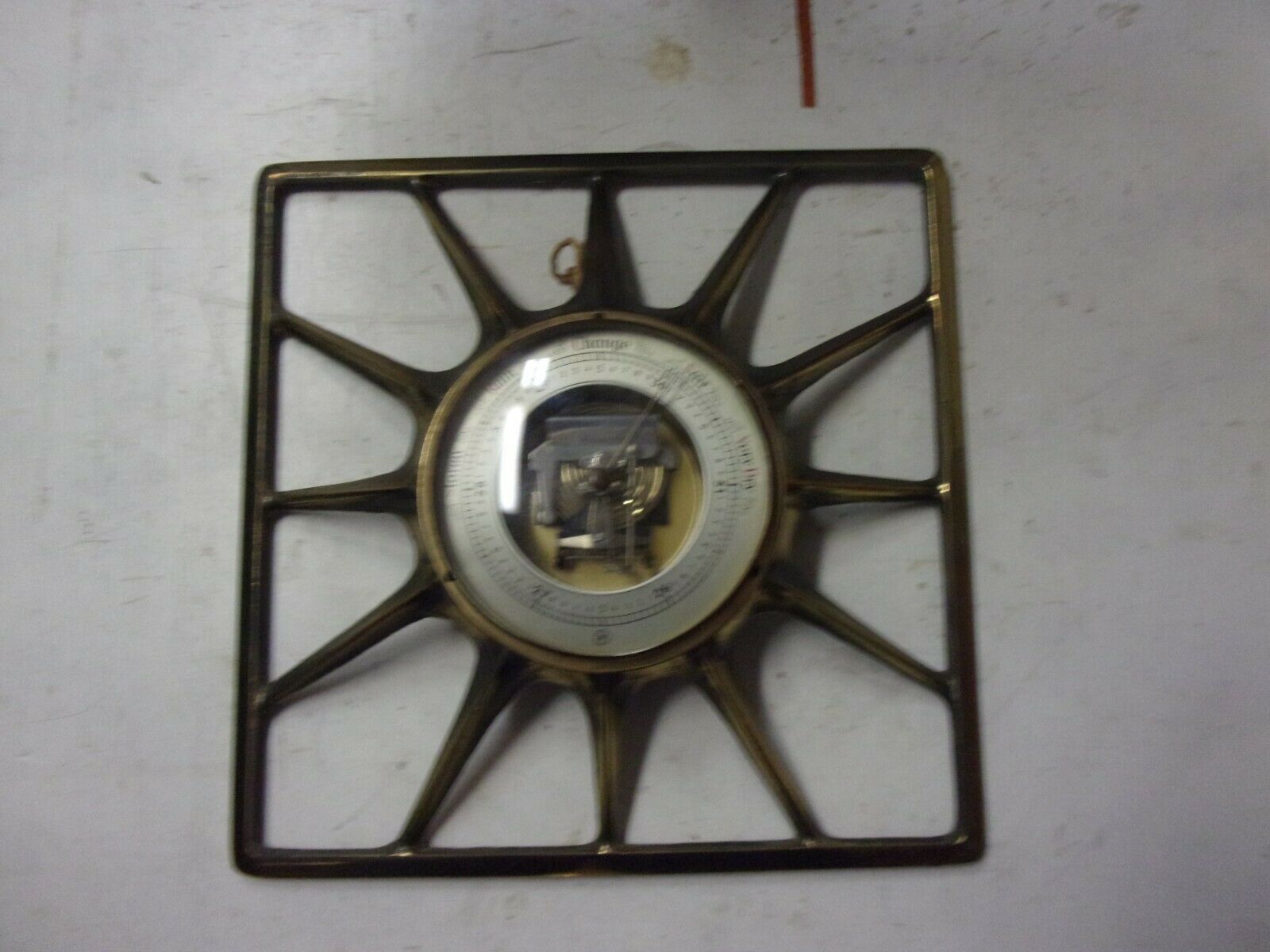
Antique Collectible Barometer Imperial wooden Russian Empire measuring device
$ 125.4
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Antique Collectible Barometer Imperial wooden Russian Empire measuring deviceDevice In working condition
Please see the photo
Diameter 14 сm
Glass diameter 8.5 cm
For the first time, the barometer was invented and described in the work “Opera geometrica” in 1644 by the scientist from Florence (Italy) Evangelista Torricelli. It was a liquid mercury barometer, the pressure of which was measured by the height of the mercury (liquid) column in a tube sealed from above, and the lower end placed in a vessel with mercury (liquid). On the day when Torriceli conducted the experiment with his mercury barometer, the weather was quiet and sunny, and the column of mercury stopped at around 760 mm. Since then, a pressure of 760 mm Hg is normal. Mercury and liquid barometers are the most accurate and are still used at meteorological stations. Their disadvantage is fragility, insecurity and large size.
In 1844, the French engineer Lucien Vidy, using the research of the 17th century German mathematics and physics. Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, designed a fundamentally new, liquid-free barometer, which was called aneroid barometer (from the Greek. "Aneros" - does not contain moisture). Barometers built on the basis of the barometer L. Vidi, at the moment, are the most common.
In general, barometers, depending on the principle of action, can be mercury, liquid, aneroid or electronic.
- Aneroid barometer - a device whose principle of action is based on changing the size of a metal box filled with rarefied air, under the action of atmospheric pressure. Such barometers are reliable and small in size.
So, the aneroid barometer is a device that is designed to measure atmospheric pressure mechanically. Structurally, the aneroid consists of a round metal (nickel-silver or hardened steel) box with corrugated (ribbed) bases, in which, by evacuating air, a strong vacuum, a return spring, a transmission mechanism and an arrow pointer are created. Under the action of atmospheric pressure: its increase or decrease, the box, respectively, is either compressed or unbent. At the same time, when compressing the bellows box, the upper flexing surface begins to pull the spring attached to it downwards, and when the atmospheric pressure decreases, the upper part, on the contrary, bends and pushes the spring upwards. An arrow is attached to the return spring using a transmission mechanism, which moves on a scale calibrated in accordance with the readings of a mercury barometer (Figure). It is worth noting that, in practice, several (up to 10 pieces) series of thin-walled corrugated boxes with a discharge are applied in series, which increases the amplitude of the arrow on the scale.
Aneroid barometers, due to their small size and lack of fluid in the structure, are the most convenient and portable; they are widely used in practice.
On request, send additional photos
Please, do not hesitate to ask all questions before purchasing.
AIR Standard International Shipping (14 to 30 days)
* without taking into account possible delays at customs